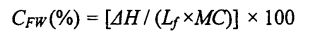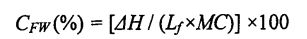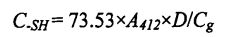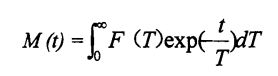ਵਿਸ਼ਾ - ਸੂਚੀ
1.1.6 ਫ੍ਰੋਜ਼ਨ ਆਟੇ ਦੀ ਗੁਣਵੱਤਾ ਵਿੱਚ ਸੁਧਾਰ ਵਿੱਚ ਹਾਈਡ੍ਰੋਕੋਲੋਇਡ ਦੀ ਵਰਤੋਂ ......................5
1.1.7 Hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose (Hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose, I-IPMC) ………. 5
2.3 Experimental results and discussion…………………………………………………………………… . 11
3.2.1 ਪ੍ਰਯੋਗਾਤਮਕ ਸਮੱਗਰੀ ......................................................................... 25
3.2.4 Experimental methods ....................................................................................................... 25
3.3.2 The effect of adding amount of HPMC and freezing storage time on the freezable moisture content (CFW) and thermal stability……………………………………………………………………. 30
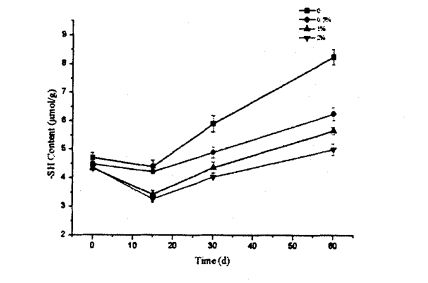
3.3.3 Effects of HPMC addition amount and freezing storage time on free sulfhydryl content (C vessel) …………………………………………………………………………………………………………. . 34
4.1 Introduction .............................................................................................................................. . 44
4.2 Experimental materials and methods ................................................................................. 45
4.2.1 ਪ੍ਰਯੋਗਾਤਮਕ ਸਮੱਗਰੀ .................................................................................... .45
4.3 Analysis and discussion ........................................................................................................... 48
ਕਣਕ ਸਟਾਰਚ ਦੇ ਮੁ basic ਲੇ ਹਿੱਸਿਆਂ ਦੀ ਸਮੱਗਰੀ ........................................................ 48
4.3.3 Effects of HPMC addition and freezing storage time on the shear viscosity of starch paste………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 52
4.3.6 Effects of I-IPMC addition amount and frozen storage time on the thermodynamic properties of starch ………………………………………………………………………………………………………. . 57
Chapter 5 Effects of HPMC addition on yeast survival rate and fermentation activity under frozen storage conditions………………………………………………………………………………………………. . 62
5.1Introduction .................................................................................................................................... 62
5.2 Materials and methods ............................................................................................................ 62
5.2.2 ਪ੍ਰਯੋਗਾਤਮਕ methods ੰਗ. . . . . ............................................................................ 63
5.3 Results and Discussion ............................................................................................................... 64
5.3.3 The effect of adding amount of HPMC and freezing time on the content of glutathione in dough……………………………………………………………………………………………………………66. "
5.4 Chapter Summary ........................................................................................................................ 67
6.1 Conclusion ................................................................................................................................. . 68
6.2 Outlook .......................................................................................................................................... 68
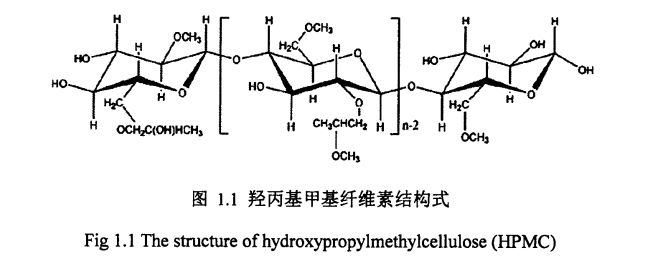
Figure 1.1 The structural formula of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose………………………. . 6
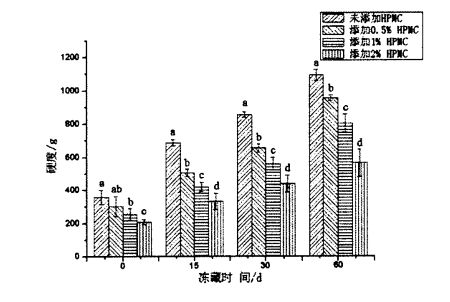
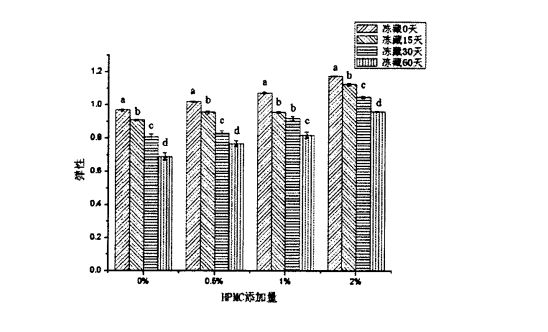
Figure 2.4 The effect of HPMC addition and freezing time on the elasticity of steamed bread………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. . 20
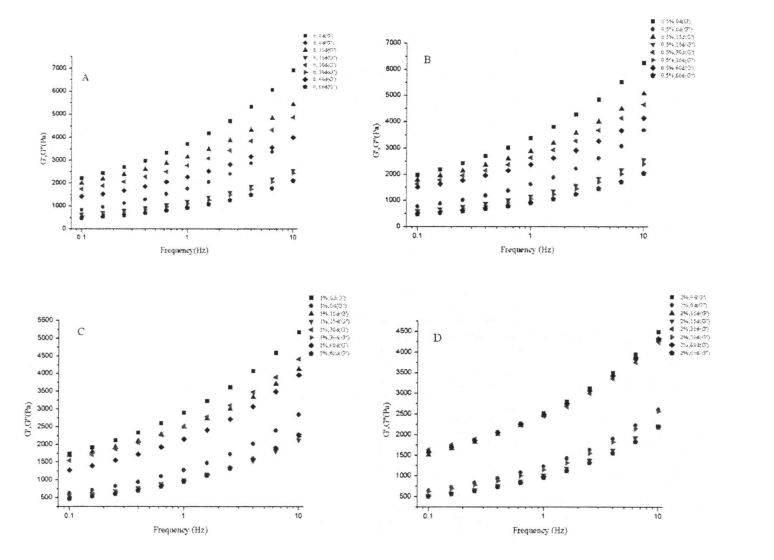
Figure 3.1 The effect of HPMC addition and freezing time on the rheological properties of wet gluten…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 30
Figure 3.2 Effects of HPMC addition and freezing time on the thermodynamic properties of wheat gluten………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. . 34
Figure 3.3 Effects of HPMC addition and freezing time on free sulfhydryl content of wheat gluten……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………... . 35
Figure 3.7 The effect of HPMC addition and freezing time on the microscopic gluten network structure…………………………………………………………………………………………………………... . 43
Figure 4.1 Starch gelatinization characteristic curve ............................................................... 51
ਚਿੱਤਰ 4.2 ਸਟਾਰਚ ਪੇਸਟ ਦਾ ਤਰਲ ਚੱਟਾਨ .................................................................................. 52
Figure 4.3 Effects of adding amount of MC and freezing time on the viscoelasticity of starch paste……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………... . 57
Figure 4.5 Effects of HPMC addition and freezing storage time on the thermodynamic properties of starch…………………………………………………………………………………………………………. . 59
Figure 5.2 The effect of HPMC addition and freezing time on the yeast survival rate…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………... . 67
Figure 5.3 Microscopic observation of yeast (microscopic examination) …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 68
ਟੇਬਲ 2.1 ਕਣਕ ਦੇ ਆਟੇ ਦਾ ਮੁ agled ਲੀ ਸਮੱਗਰੀ ਦੀ ਸਮੱਗਰੀ .................................................. 11
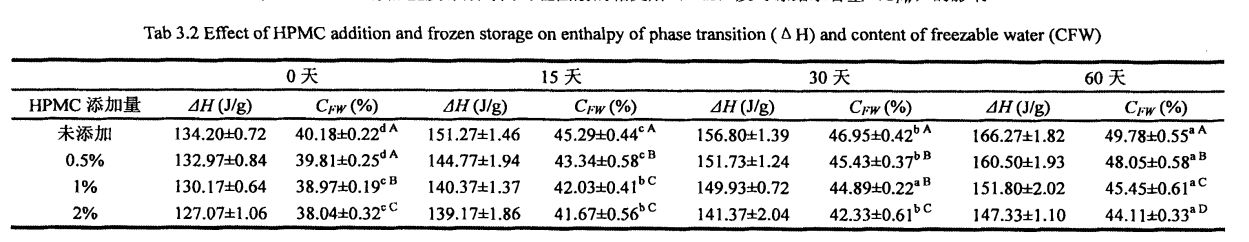
Table 3.2 Effects of I-IPMC addition amount and freezing storage time on the phase transition enthalpy (Yi IV) and freezer water content (e chat) of wet gluten………………………. 31
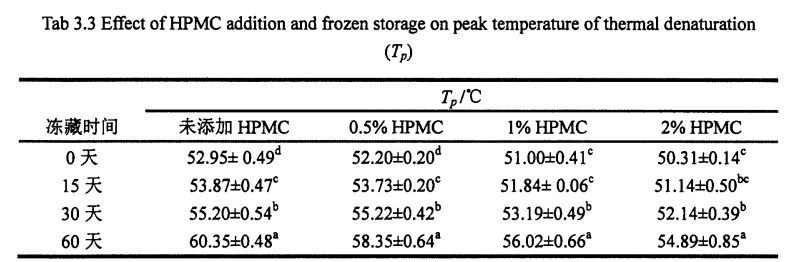
Table 3.3 Effects of HPMC addition amount and freezing storage time on the peak temperature (product) of thermal denaturation of wheat gluten…………………………………………. 33
Table 3.6 Effects of I-IPMC addition and freezing storage time on the surface hydrophobicity of wheat gluten……………………………………………………………………………………………. 41
Table 4.3 Effects of I-IPMC addition and freezing time on the shear viscosity of wheat starch paste…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 55
5)Preservation and anti-aging of steamed bread and related mechanisms. Pan Lijun et al. (2010) optimized the composite modifier with good anti-aging effect through experimental design [l do not; ਵੈਂਗ, ਏ ਟੀ ਏ 1. (2015) studied the effects of gluten protein polymerization degree, moisture, and starch recrystallization on the increase of steamed bread hardness by analyzing the physical and chemical properties of steamed bread. ਨਤੀਜਿਆਂ ਨੇ ਦਿਖਾਇਆ ਕਿ ਪਾਣੀ ਦਾ ਨੁਕਸਾਨ ਅਤੇ ਸਟਾਰਚ ਪ੍ਰਤਿਭਾਸ਼ਾਲੀ ਰੋਟੀ ਦੇ ਬੁ aging ਾਪੇ ਦੇ ਮੁੱਖ ਕਾਰਨ ਸਨ [20].
6)Research on the application of new fermented bacteria and sourdough. Jiang, et a1. (2010) Application of Chaetomium sp. ਭੁੰਲਨ ਵਾਲੀ ਰੋਟੀ ਵਿੱਚ ਐਕਸਲਲੇਨਜ (ਥਰਮਾਸਟੇਬਲ) ਤਿਆਰ ਕਰਨ ਲਈ. Gerez, eta 1. (2012) used two kinds of lactic acid bacteria in fermented flour products and evaluated their quality [221; Wu, et al. (2012) studied the influence of sourdough fermented by four kinds of lactic acid bacteria (Lactobacillus plantarum, Lactobacillus, sanfranciscemis , Lactobacillus brevis and Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp bulgaricus) on the quality (specific volume, texture, fermentation flavor, etc.) of northern steamed bread [23]; and Gerez, et a1. (2012) used the fermentation characteristics of two kinds of lactic acid bacteria to accelerate the hydrolysis of gliadin to reduce the allergenicity of flour products [24] and other aspects.
Among them, steamed bread is prone to aging under conventional storage conditions, which is an important factor restricting the development of steamed bread production and processing industrialization. After aging, the quality of steamed bread is reduced - the texture becomes dry and hard, dregs, shrinks and cracks, the sensory quality and flavor deteriorate, the digestion and absorption rate decreases, and the nutritional value decreases. ਇਹ ਸਿਰਫ ਇਸ ਦੇ ਸ਼ੈਲਫ ਲਾਈਫ ਨੂੰ ਪ੍ਰਭਾਵਤ ਨਹੀਂ ਕਰਦਾ, ਬਲਕਿ ਬਹੁਤ ਸਾਰਾ ਕੂੜਾ ਵੀ ਪੈਦਾ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ. ਅੰਕੜਿਆਂ ਦੇ ਅਨੁਸਾਰ, ਉਮਰ ਦੇ ਕਾਰਨ ਸਾਲਾਨਾ ਘਾਟਾ ਆਟੇ ਦੇ ਉਤਪਾਦਾਂ ਦੇ ਆਉਟਪੁੱਟ ਦਾ 3% ਹੈ. 7%. With the improvement of people's living standards and health awareness, as well as the rapid development of the food industry, how to industrialize the traditional popular staple noodle products including steamed bread, and obtain products with high quality, long shelf life and easy preservation to meet the needs of the growing demand for fresh, safe, high-quality and convenient food is a long-standing technical problem. Based on this background, frozen dough came into being, and its development is still in the ascendant.
ਏ) ਫ੍ਰੋਜ਼ਨ ਆਟੇ ਦਾ method ੰਗ: ਤੇਜ਼-ਜੰਮਿਆ ਹੋਇਆ, ਜੰਮੇ ਹੋਏ, ਪਿਘਲ, ਪਰੂਫਡ, ਅਤੇ ਪਕਾਏ ਜਾਣ (ਪਕਾਉਣਾ, ਭਾਫ, ਆਦਿ) ਵਿੱਚ ਵੰਡਿਆ ਗਿਆ ਹੈ
Most studies have found that the formation and growth of ice crystals in frozen foods is an important factor leading to the deterioration of product quality [291]. Ice crystals not only reduce the survival rate of yeast, but also weaken the gluten strength, affect the starch crystallinity and gel structure, and damage the yeast cells and release the reducing glutathione, which further reduces the gas holding capacity of gluten. In addition, in the case of frozen storage, temperature fluctuations can cause ice crystals to grow due to recrystallization [30]. Therefore, how to control the adverse effects of ice crystal formation and growth on starch, gluten and yeast is the key to solving the above problems, and it is also a hot research field and direction. ਪਿਛਲੇ ਦਸ ਸਾਲਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ, ਬਹੁਤ ਸਾਰੇ ਖੋਜਕਰਤਾ ਇਸ ਕੰਮ ਵਿੱਚ ਲੱਗੇ ਹੋਏ ਹਨ ਅਤੇ ਕੁਝ ਫਲਦਾਇਕ ਖੋਜ ਨਤੀਜੇ ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤ ਕੀਤੇ ਹਨ. However, there are still some gaps and some unresolved and controversial issues in this field, which need to be further explored, such as:
i.Study the changes in the structure and properties of frozen dough with the extension of freezing storage time, in order to explore the reasons for the deterioration of product quality, especially the effect of ice crystallization on biological macromolecules (protein, starch, etc.), for example, ice crystallization. ਗਠਨ ਅਤੇ ਵਿਕਾਸ ਅਤੇ ਪਾਣੀ ਦੀ ਅਵਸਥਾ ਅਤੇ ਵੰਡ ਨਾਲ ਇਸ ਦਾ ਸੰਬੰਧ; changes in wheat gluten protein structure, conformation and properties [31]; changes in starch structure and properties; changes in dough microstructure and related properties, etc. 361.
ਅਧਿਐਨ ਨੇ ਦਿਖਾਇਆ ਹੈ ਕਿ ਜੰਮਣ ਆਟੇ ਦੀ ਪ੍ਰੋਸੈਸਿੰਗ ਦੀਆਂ ਵਿਸ਼ੇਸ਼ਤਾਵਾਂ ਦੇ ਵਿਗਾੜ ਦੇ ਮੁੱਖ ਕਾਰਨਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਸ਼ਾਮਲ ਹਨ: 1) ਠੰ. ਦੀ ਪ੍ਰਕਿਰਿਆ ਦੌਰਾਨ, ਖਮੀਰ ਦੀ ਪ੍ਰਕਿਰਿਆ ਦੌਰਾਨ, ਖਮੀਰ ਅਤੇ ਇਸ ਦੀ ਫਰਮੈਂਟੇਸ਼ਨ ਗਤੀਵਿਧੀ ਦੇ ਬਚਾਅ ਵਿੱਚ ਕਾਫ਼ੀ ਘੱਟ ਗਏ ਹਨ; 2) The continuous and complete network structure of the dough is destroyed, resulting in the air holding capacity of the dough. and the structural strength is greatly reduced.
II. Optimization of frozen dough production process, frozen storage conditions and formula. During the production of frozen dough, temperature control, proofing conditions, pre-freezing treatment, freezing rate, freezing conditions, moisture content, gluten protein content, and thawing methods will all affect the processing properties of frozen dough [37]. In general, higher freezing rates produce ice crystals that are smaller in size and more uniformly distributed, while lower freezing rates produce larger ice crystals that are not uniformly distributed. In addition, a lower freezing temperature even below the glass transition temperature (CTA) can effectively maintain its quality, but the cost is higher, and the actual production and cold chain transportation temperatures are usually small. In addition, the fluctuation of the freezing temperature will cause recrystallization, which will affect the quality of the dough.
III. Using additives to improve the product quality of frozen dough. In order to improve the product quality of frozen dough, many researchers have made explorations from different perspectives, for example, improving the low temperature tolerance of material components in frozen dough, using additives to maintain the stability of the dough network structure [45.56], etc. Among them, the use of additives is an effective and widely used method. Mainly include, i) enzyme preparations, such as, transglutaminase, O [. Amylase; ii) emulsifiers, such as monoglyceride stearate, DATEM, SSL, CSL, DATEM, etc.; iii) antioxidants, ascorbic acid, etc.; iv) polysaccharide hydrocolloids, such as guar gum, yellow Originalgum, gum Arabic, konjac gum, sodium alginate, etc.; v) other functional substances, such as Xu, et a1. (2009) added Ice-structuring Proteins to wet gluten mass under freezing conditions, and studied its protective effect and mechanism on the structure and function of gluten protein [y71.
1.6.6.6.6.6.6.600 ਡਾਲਰ ਦੀ ਗੁਣਵੱਤਾ ਦੇ ਸੁਧਾਰ ਵਿੱਚ ਹਾਈਡ੍ਰੋਕੋਇਡਜ਼ ਦਾ
Due to the existence of hydrogen bonds in the linear molecular chain and crystalline structure, cellulose has poor water solubility, which also limits its application range. ਹਾਲਾਂਕਿ, ਐਚਪੀਐਮਸੀ ਦੀ ਸਾਈਡ ਚੇਨ 'ਤੇ ਬਦਲਾਵਰਾਂ ਦੀ ਮੌਜੂਦਗੀ ਇੰਟ੍ਰੋਮੋਲਕੂਲਰ ਹਾਈਡ੍ਰੋਜਨ ਬਾਂਡਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਤੋੜਦੀ ਹੈ, ਇਸ ਨੂੰ ਵਧੇਰੇ ਹਾਈਡ੍ਰੋਬਿਲਿਕ [66L], ਜੋ ਕਿ ਘੱਟ ਤਾਪਮਾਨ ਵਿਚ ਤੇਜ਼ੀ ਨਾਲ ਸੋਜ ਸਕਦੀ ਹੈ. As a cellulose derivative-based hydrophilic colloid, HPMC has been widely used in the fields of materials, papermaking, textiles, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals and food [6 71]. In particular, due to its unique reversible thermo-gelling properties, HPMC is often used as a capsule component for controlled release drugs; in food, HPMC is also used as a surfactant, Thickeners, emulsifiers, stabilizers, etc., and play a role in improving the quality of related products and realizing specific functions. For example, the addition of HPMC can change the gelatinization characteristics of starch and reduce the gel strength of starch paste. , HPMC can reduce the loss of moisture in food, reduce the hardness of bread core, and effectively inhibit the aging of bread.
At present, the application and large-scale production of frozen dough processing technology in my country as a whole is still in the development stage. At the same time, there are certain pitfalls and deficiencies in the frozen dough itself. ਇਹ ਵਿਆਪਕ ਕਾਰਕ ਬਿਨਾਂ ਸ਼ੱਕ ਨੂੰ ਜੰਮੇ ਹੋਏ ਆਟੇ ਦੇ ਅਗਲੇ ਕਾਰਜ ਨੂੰ ਸੀਮਤ ਕਰਦੇ ਹਨ. on the other hand,this also means that the application of frozen dough has great potential and broad prospects, especially from the perspective of combining frozen dough technology with the industrialized production of traditional Chinese noodles (non-)fermented staple food, to develop more products that meet the needs of Chinese residents. It is of practical significance to improve the quality of the frozen dough based on the characteristics of Chinese pastry and the dietary habits, and is suitable for the processing characteristics of Chinese pastry.
ਇਹ ਆਮ ਤੌਰ ਤੇ ਮੰਨਿਆ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ਕਿ ਆਟੇ ਇੱਕ ਖਾਸ ਕੰਪਲਾਇਜ਼, ਮਲਟੀ-ਇੰਟਰਫੇਸ, ਮਲਟੀ-ਇੰਟਰਫੇਸ, ਮਲਟੀ-ਪੜਾਅ ਅਤੇ ਮਲਟੀ-ਪੈਮਾਨੇ ਦੀਆਂ ਵਿਸ਼ੇਸ਼ਤਾਵਾਂ ਹਨ.
1) ਇੱਕ ਨਵੀਂ ਕਿਸਮ ਦੀ ਹਾਈਡ੍ਰੋਫਿਲਿਕ ਕੋਲੋਇਡ, ਹਾਈਡਰੋਕਪ੍ਰੋਪੀਲ ਮੈਥਾਈਲਸੈਲੂਲੂਲੋਜ਼ (ਐਚਪੀਐਮਸੀ) ਨੂੰ ਇੱਕ ਐਡਪੇਟ ਵਜੋਂ ਚੁਣੋ ਅਤੇ ਐਚਪੀਐਮਪੀਓ ਨੂੰ ਵੱਖ ਵੱਖ ਠੰ. ਤੋਂ ਇਲਾਵਾ) ਸ਼ਰਤਾਂ ਦਾ ਅਧਿਐਨ ਕਰੋ. (0%, 0.5%, 1%, 2%; the same below) on the rheological properties and microstructure of frozen dough, as well as on the quality of the dough product - steamed bread (including the specific volume of steamed bread) , texture), investigate the effect of adding HPMC to the frozen dough on the processing properties of the dough and the quality of steamed bread, and evaluate the improvement effect of HPMC on the processing properties of the frozen dough;
Generally speaking, the material composition of dough used for making fermented flour products mainly includes biological macromolecular substances (starch, protein), inorganic water, and yeast of organisms, and is formed after hydration, cross-linking and interaction. A stable and complex material system with a special structure has been developed. Numerous studies have shown that the properties of the dough have a significant impact on the quality of the final product. ਇਸ ਲਈ, ਖਾਸ ਉਤਪਾਦ ਨੂੰ ਪੂਰਾ ਕਰਨ ਲਈ ਮਿਸ਼ਰਿਤ ਨੂੰ ਅਨੁਕੂਲ ਬਣਾ ਕੇ ਅਤੇ ਵਰਤੋਂ ਲਈ ਭੋਜਨ ਦੀ ਗੁਣਵਤਾ ਦੀ ਆਟੇ ਜਾਂ ਟੈਕਨੋਲੋਜੀ ਨੂੰ ਬਿਹਤਰ ਬਣਾਉਣ ਲਈ ਇਹ ਇਕ ਰਿਸਰਚ ਦਿਸ਼ਾ ਹੈ; on the other hand, improving or improving the properties of dough processing and preservation to ensure or improve the quality of the product is also an important research issue.
ਡੀਐਚਜੀ. 9070A Blast Drying Oven
Powder meter. ਈ
Extensometer. ਈ
FD. 1 ਬੀ. 50 Vacuum Freeze Dryer
ਨਿਰਮਾਤਾ
ਹੰਗ ਸ਼ੀਗ ਫੈਂਗ ਮੈਡੀਕਲ ਉਪਕਰਣਾਂ ਦੀ ਕੰਪਨੀ ਕੰਪਨੀ, ਲਿਮਟਿਡ
ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਵਿਚੋਂ, ਨਮੀ ਦੇ ਅਕਾਲੀ ਨਮੀ ਦੀ ਗਰਮੀ ਨੂੰ ਦਰਸਾਉਂਦਾ ਹੈ, ਅਤੇ ਇਸਦਾ ਮੁੱਲ 334 Jan ਹੈ; MC (total Moisture Content) represents the total moisture content in the dough (measured according to GB 50093.2010t78]). Each sample was repeated three times.
All experiments were repeated at least three times unless otherwise specified, and the experimental results were expressed as the mean (Mean) ± standard deviation (Standard Deviation). ਐਸਪੀਐਸ ਸਟੈਟਿਸਟਿਕ 19 ਦੀ ਵਰਤੋਂ ਪਰਿਵਰਤਨ ਦੇ ਵਿਸ਼ਲੇਸ਼ਣ ਲਈ ਕੀਤੀ ਗਈ ਸੀ ਸਹੀ ਚਾਰਟ ਖਿੱਚਣ ਲਈ ਮੂਲ 8.0 ਦੀ ਵਰਤੋਂ ਕਰੋ.
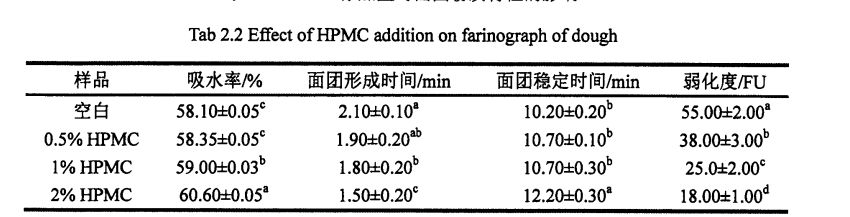
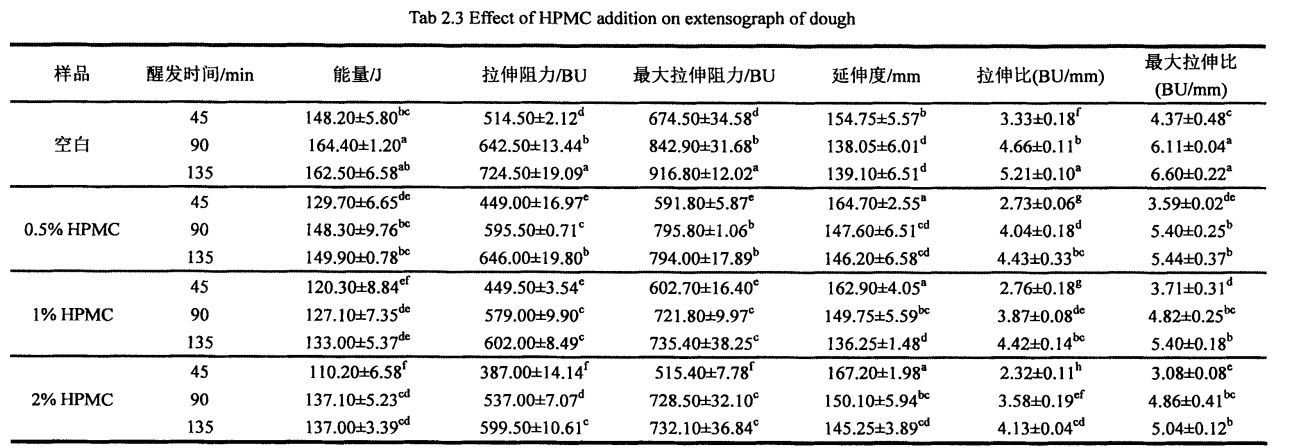
As shown in Table 2.2, with the increase of HPMC addition, the water absorption of dough increased significantly, from 58.10% (without adding HPMC dough) to 60.60% (adding 2% HPMC dough). ਇਸ ਤੋਂ ਇਲਾਵਾ ਐਚਪੀਐਮਸੀ ਦੇ ਜੋੜ ਨੇ ਆਟੇ ਦੇ 10.2 ਮਿਨ (ਖਾਲੀ) ਤੋਂ 12.2 ਮਿੰਟ ਤੱਕ ਸੁਧਾਰ ਕੀਤਾ (2% ਐਚਪੀਪੀ 0 ਸੀ). However, with the increase of HPMC addition, both the dough forming time and the dough weakening degree decreased significantly, from the blank dough forming time of 2.10 min and the weakening degree of 55.0 FU, respectively, to the addition of 2% HPMC, the dough forming time was 1. .50 min and weakening degree of 18.0 FU, decreased by 28.57% and 67.27%, respectively.
Because HPMC has strong water retention and water holding capacity, and is more absorbent than wheat starch and wheat gluten [8"01, therefore, the addition of HPMC improves the water absorption rate of the dough. The dough forming time is when the dough consistency reaches 500 The time required for FU, the addition of HPMC reduces the dough formation time, which indicates that the addition of HPMC promotes the formation of the dough. The dough stability time is the time when the dough consistency is maintained above 500 FU, and HPMC increases the dough stability time, which is due to the dough It is caused by the shortening of the forming time and the relative stability of the dough consistency. The degree of weakening represents the difference between the maximum consistency of the dough and the final consistency, and the reduction of the weakening degree of the dough by HPMC shows ਕਿ ਐਚਪੀਐਮਸੀ ਆਟੇ ਦੀ ਇਕਸਾਰਤਾ ਨੂੰ ਸਥਿਰ ਕਰਨ ਵਿਚ ਭੂਮਿਕਾ ਨਿਭਾ ਸਕਦਾ ਹੈ. ਆਟੇ ਸਥਿਰਤਾ ਦਾ ਸਮਾਂ ਐਚਪੀਐਮਸੀ ਦੇ ਵਾਧੇ ਨੂੰ ਦਰਸਾਉਂਦਾ ਹੈ, ਅਤੇ ਇਹ ਨਤੀਜੇ ਰੋਸਲ, ਕਾਲਰ, ਅਤੇ ਹਰੋਸ (2007) ਦੇ ਖੋਜ ਨਤੀਜਿਆਂ ਦੇ ਅਨੁਸਾਰ ਹਨ.
However, the addition of HPMC can effectively suppress the above trend and change the tensile properties of the dough. With the increase of HPMC addition, the tensile resistance, maximum tensile resistance and energy value of the dough all decreased correspondingly, while the elongation increased. ਖਾਸ ਤੌਰ 'ਤੇ, ਜਦੋਂ ਪਰੂਫਾਂ ਦਾ ਸਮਾਂ 45 ਮਿੰਟ ਦਾ ਵਾਧਾ ਹੋਇਆ, ਐਚਪੀਐਮਸੀ ਦਾ ਵਾਧਾ ਕ੍ਰਮਵਾਰ ਘਟਿਆ: 6.8.30 ± 8.84 ਜੇ), ਅਤੇ 110.20-ਏ: 6.58
The specific volume of steamed bread can better reflect the appearance and sensory quality of steamed bread. The larger the specific volume of the steamed bread, the larger the volume of the steamed bread of the same quality, and the specific volume has a certain influence on the appearance, color, texture, and sensory evaluation of the food. ਆਮ ਤੌਰ 'ਤੇ ਬੋਲਣਾ, ਵੱਡੀ ਖਾਸ ਵਾਲੀਅਮ ਵਾਲੇ ਭੁੰਲਨ ਵਾਲੇ ਬਾਂਸ ਵੀ ਕੁਝ ਹੱਦ ਤਕ ਵਧੇਰੇ ਪ੍ਰਸਿੱਧ ਹਨ.
The specific volume of steamed bread can better reflect the appearance and sensory quality of steamed bread. The larger the specific volume of the steamed bread, the larger the volume of the steamed bread of the same quality, and the specific volume has a certain influence on the appearance, color, texture, and sensory evaluation of the food. ਆਮ ਤੌਰ 'ਤੇ ਬੋਲਣਾ, ਵੱਡੀ ਖਾਸ ਵਾਲੀਅਮ ਵਾਲੇ ਭੁੰਲਨ ਵਾਲੇ ਬਾਂਸ ਵੀ ਕੁਝ ਹੱਦ ਤਕ ਵਧੇਰੇ ਪ੍ਰਸਿੱਧ ਹਨ.
Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) is a kind of hydrophilic colloid, and its application research in frozen dough with Chinese-style pasta food (such as steamed bread) as the final product is still lacking. The main purpose of this study is to evaluate the effect of HPMC improvement by investigating the effect of HPMC addition on the processing properties of frozen dough and the quality of steamed bread, so as to provide some theoretical support for the application of HPMC in steamed bread and other Chinese-style flour products. The results show that HPMC can improve the farinaceous properties of the dough. When the addition amount of HPMC is 2%, the water absorption rate of the dough increases from 58.10% in the control group to 60.60%; 2 ਮਿੰਟ ਵਧ ਕੇ 12.2 ਮਿੰਟ; at the same time, the dough formation time decreased from 2.1 min in the control group to 1.5 mill; the weakening degree decreased from 55 FU in the control group to 18 FU. In addition, HPMC also improved the tensile properties of the dough. With the increase in the amount of HPMC added, the elongation of the dough increased significantly; significantly reduced. In addition, during the frozen storage period, the addition of HPMC reduced the increase rate of the freezable water content in the dough, thereby inhibiting the damage to the dough network structure caused by ice crystallization, maintaining the relative stability of the dough viscoelasticity and the integrity of the network structure, thereby improving the stability of the dough network structure. The quality of the final product is guaranteed.
For frozen dough, under freezing conditions, the formation and growth of ice crystals (crystallization and recrystallization process) will cause the dough network structure to be physically squeezed, and its structural integrity will be destroyed, and microscopically. Accompanied by changes in the structure and properties of gluten protein [105'1061. As Zhao, et a1. (2012) found that with the prolongation of freezing time, the molecular weight and molecular gyration radius of gluten protein decreased [107J, which indicated that gluten protein partially depolymerized. ਇਸ ਤੋਂ ਇਲਾਵਾ, ਸਪੈਟੀਅਲ ਅਨੁਕੂਲ ਬਦਲਾਅ ਅਤੇ ਗਲੂਟਨ ਪ੍ਰੋਟੀਨ ਦੀਆਂ ਥਰਮੋਡਾਇਨਾਮਿਕ ਵਿਸ਼ੇਸ਼ਤਾ ਆਟੇ ਪ੍ਰੋਸੈਸਿੰਗ ਵਿਸ਼ੇਸ਼ਤਾਵਾਂ ਅਤੇ ਉਤਪਾਦਾਂ ਦੀ ਗੁਣਵੱਤਾ ਨੂੰ ਪ੍ਰਭਾਵਤ ਕਰੇਗੀ. ਇਸ ਲਈ, ਠੰ .ਾ ਸਟੋਰੇਜ ਦੀ ਪ੍ਰਕਿਰਿਆ ਵਿਚ, ਇਸ ਨੂੰ ਕੁਝ ਖੋਜ ਦੀ ਜਾਂਚ ਕਰਨ ਲਈ, ਵੱਖ-ਵੱਖ ਠੱਗ ਸਟੋਰਾਂ ਦੇ ਅਧੀਨ structure ਾਂਚੇ ਅਤੇ ਵਿਸ਼ੇਸ਼ਤਾਵਾਂ ਦੀ structure ਾਂਚੇ ਅਤੇ ਗਲੂਟਨ ਪ੍ਰੋਟੀਨ ਦੇ structure ਾਂਚੇ ਅਤੇ ਵਿਸ਼ੇਸ਼ਤਾਵਾਂ ਦੀ structure ਾਂਚੇ ਅਤੇ ਵਿਸ਼ੇਸ਼ਤਾਵਾਂ ਦੀ ਪ੍ਰਤੱਖਤਾ ਦੀਆਂ ਵਿਸ਼ੇਸ਼ਤਾਵਾਂ.
FD. 1 ਬੀ. 50 Vacuum Freeze Dryer
ਨਿਰਮਾਤਾ
ਥਰਮੂ ਫਿਸ਼ਰ, ਅਮਰੀਕਾ
ਥਰਮੂ ਫਿਸ਼ਰ, ਅਮਰੀਕਾ
(2) ਕਣਕ ਦੇ ਗਲੂਟਨ ਪ੍ਰੋਟੀਨ ਦੇ ਥਰਮਲ ਡਨੇਰਟਮੈਂਟ ਦਾ ਨਿਰਣਾਇਕ
Among them, 73.53 is the extinction coefficient; A is the absorbance value; ਡੀ ਵਿਲੱਖਣਤਾ ਦਾ ਕਾਰਕ ਹੈ (1 ਇੱਥੇ 1); G ਪ੍ਰੋਟੀਨ ਇਕਾਗਰਤਾ ਹੈ. ਹਰ ਨਮੂਨੇ ਨੂੰ ਤਿੰਨ ਵਾਰ ਦੁਹਰਾਇਆ ਗਿਆ ਸੀ.
ਲਾਅਪਲੇਸ ਇਨਵਰਸ ਟ੍ਰਾਂਸਫੋਰਸ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ ਮਿਲ ਕੇ ਮੁਹਾਣੀਕਰਤਾ ਵਿਸ਼ਲੇਸ਼ਣ ਸਾੱਫਟਵੇਅਰ ਵਿੱਚ ਅਟਾਰਨਰ ਵਿਸ਼ਲੇਸ਼ਣ ਸਾੱਫਟਵੇਅਰ ਦੀ ਵਰਤੋਂ ਕਰਨਾ, ਉਲਟਾ ਇੱਕ ਨਿਰੰਤਰ ਵੰਡ ਕਰਵ ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤ ਕਰਨ ਲਈ ਪ੍ਰਦਰਸ਼ਨ ਕੀਤਾ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ. Each sample was repeated three times
3. ਨਤੀਜੇ ਅਤੇ ਵਿਚਾਰ-ਵਟਾਂਦਰੇ
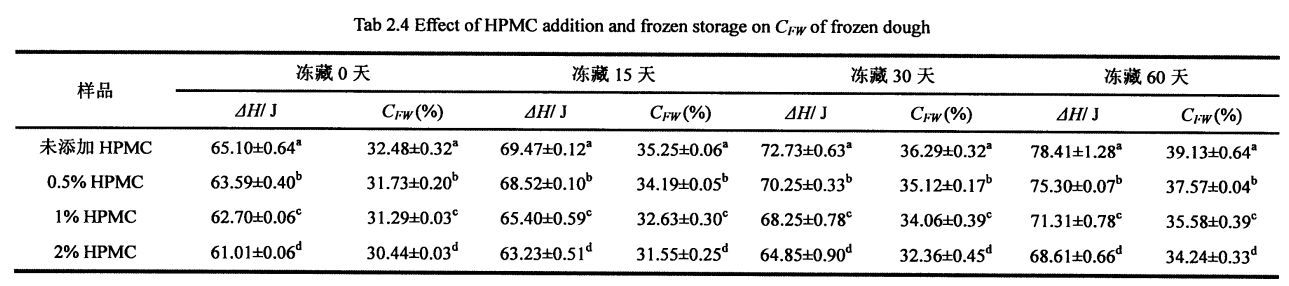
3.3.2 ਐਚਪੀਐਮਸੀ ਜੋੜਨ ਦੀ ਰਕਮ ਦੇ ਪ੍ਰਭਾਵ ਫ੍ਰੀਜ਼ਰ ਨਮੀ ਦੀ ਸਮਗਰੀ (ਸੀਐਫਡਬਲਯੂ) ਅਤੇ ਥਰਮਲ ਸਥਿਰਤਾ 'ਤੇ ਠੰ .ੇ ਸਟੋਰੇਜ ਦੇ ਸਮੇਂ
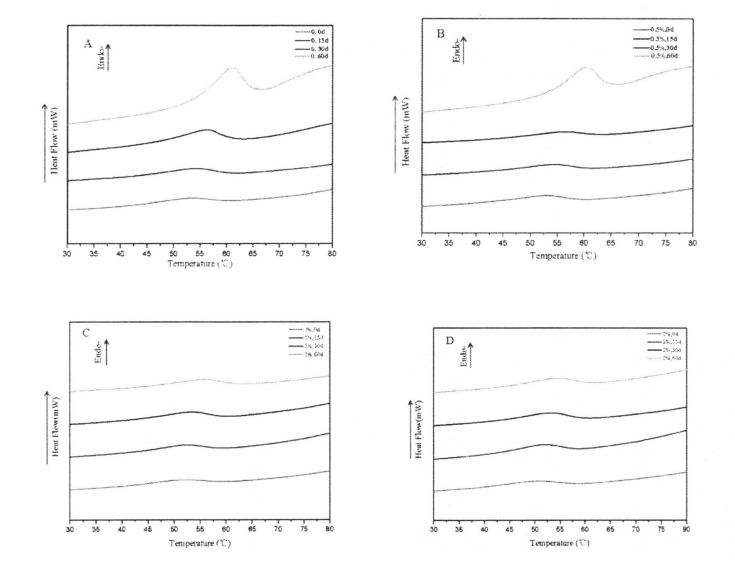
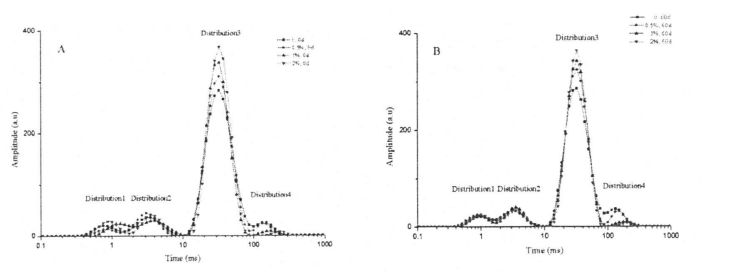
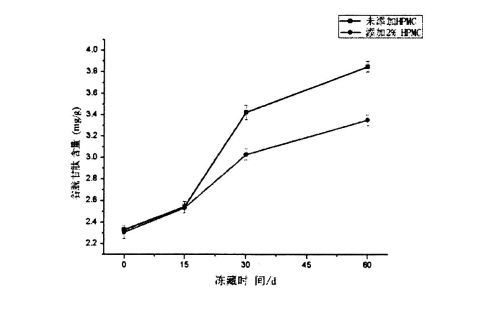
In addition, the height and area of the T24 distribution of the wet gluten mass with different contents of HPMC were significantly different (Fig. 3.4, A), and the relative content of free water was negatively correlated with the amount of HPMC added. ਇਹ ਡਾਂਗ ਵੰਡ ਦੇ ਬਿਲਕੁਲ ਉਲਟ ਹੈ. Therefore, this variation rule indicates that HPMC has water holding capacity and converts free water to confined water. ਹਾਲਾਂਕਿ, 60 ਦਿਨਾਂ ਰੁਕਣ ਤੋਂ ਬਾਅਦ, ਟੀ 24 ਦੀ ਵੰਡ ਦੀ ਉਚਾਈ ਅਤੇ ਖੇਤਰ ਵੱਖ-ਵੱਖ ਡਿਗਰੀਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਵਧਾਈ ਗਈ, ਜਿਸ ਨੇ ਸੰਕੇਤ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਕਿ ਪਾਣੀ ਦੀ ਰਾਜ ਸੀਮਤ ਪ੍ਰਕਿਰਿਆ ਤੋਂ ਮੁਕਤ ਪ੍ਰਚਲਤ ਰਾਜ ਤੋਂ ਆਜ਼ਾਦ ਵਾਰ ਤੋਂ ਮੁਕਤ-ਵਗਦੇ ਰਾਜ ਨੂੰ ਆਜ਼ਾਦ ਵਾਰ ਤੋਂ ਮੁਕਤ-ਵਗਦੇ ਰਾਜ ਤੱਕ ਪਹੁੰਚ ਗਈ. ਇਹ ਮੁੱਖ ਤੌਰ 'ਤੇ ਗਲੂਟਨ ਪ੍ਰੋਟੀਨ ਦੇ ਅਨੁਕੂਲ ਪ੍ਰੋਟੀਨ ਤਾਲਮੇਲ ਅਤੇ "ਪਰਤ" ਇਕਾਈ ਦੇ ਵਿਨਾਸ਼ ਦੇ ਕਾਰਨ ਹੈ, ਜੋ ਇਸ ਵਿਚ ਸੀਮਤ ਪਾਣੀ ਦੀ ਸਥਿਤੀ ਨੂੰ ਬਦਲਦਾ ਹੈ. Although the content of freezable water determined by DSC also increases with the extension of freezing storage time, however, due to the difference in the measurement methods and characterization principles of the two, the freezable water and free water are not completely equivalent. For the wet gluten mass added with 2% HPMC, after 60 days of freezing storage, none of the four distributions showed significant differences, indicating that HPMC can effectively retain the water state due to its own water-holding properties and its interaction with gluten. and stable liquidity.
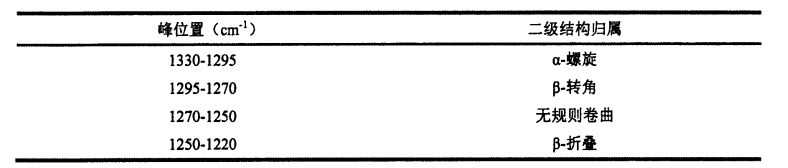
ਚਿੱਤਰ 3.5 ਕੀ ਡੈਨੁਕਵਨਵੀਸ਼ਨਿਵ ਅਤੇ ਦੂਜਾ ਡੈਰੀਵੇਟਿਵ ਦੇ ਫਿਟਿੰਗ ਦੇ ਫਿੱਟ ਹੋਣ ਤੋਂ ਬਾਅਦ 5 ਦਿਨਾਂ ਲਈ FPLC ਦੇ ਅਮਾਈਡ ਸਪੈਕਟ੍ਰਮ ਨੂੰ 0 ਦਿਨਾਂ ਲਈ HPMC ਦੇ ਵੱਖ-ਵੱਖ ਸਮੱਗਰੀ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ ਜੋੜਿਆ ਗਿਆ ਹੈ. (2001) applied the second derivative to fit the deconvoluted peaks with similar peak shapes [1321]. ਹਰੇਕ ਸੈਕੰਡਰੀ structure ਾਂਚੇ, ਟੇਬਲ 3.5 ਦੇ ਅਨੁਸਾਰੀ ਸਮਗਰੀ ਤਬਦੀਲੀਆਂ ਦੀ ਮਾਤਰਾ ਵਿੱਚ ਬਦਲਣ ਲਈ.
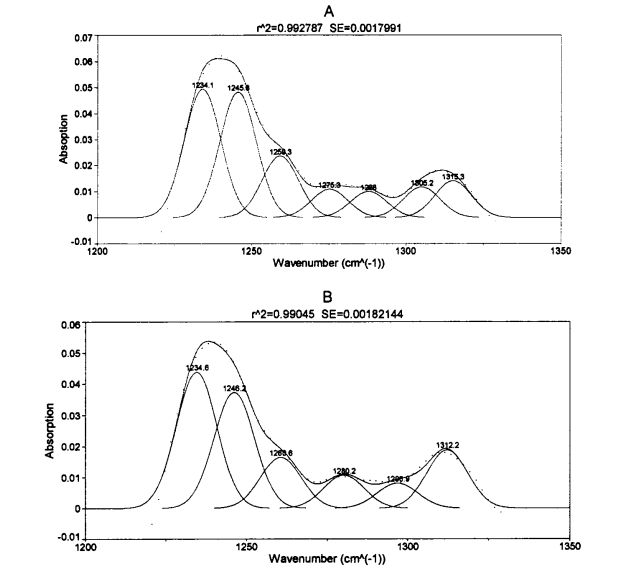
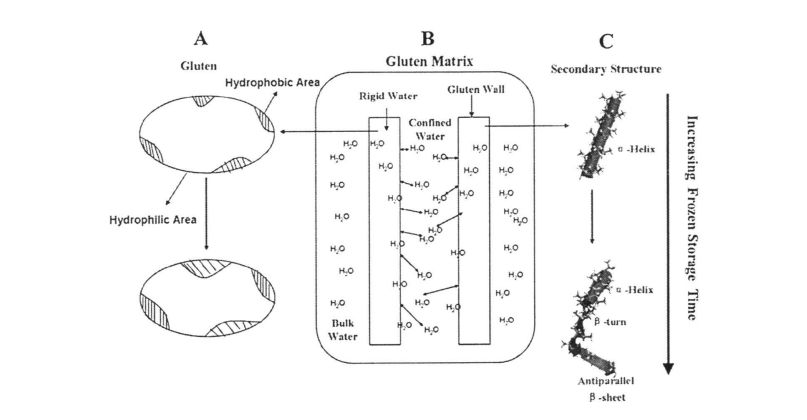
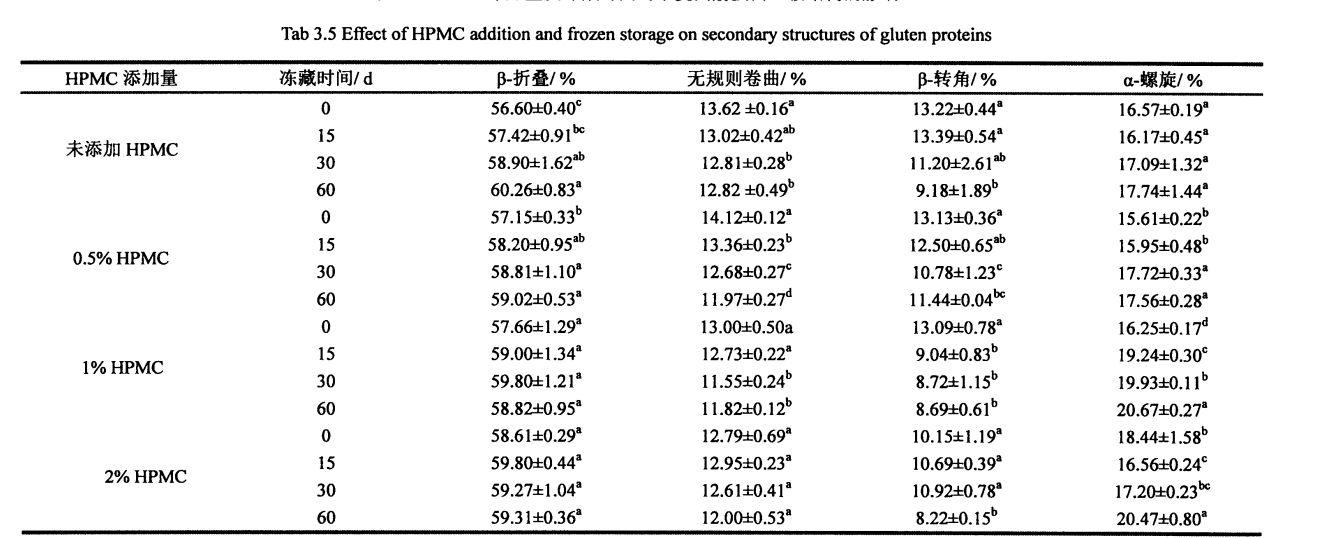

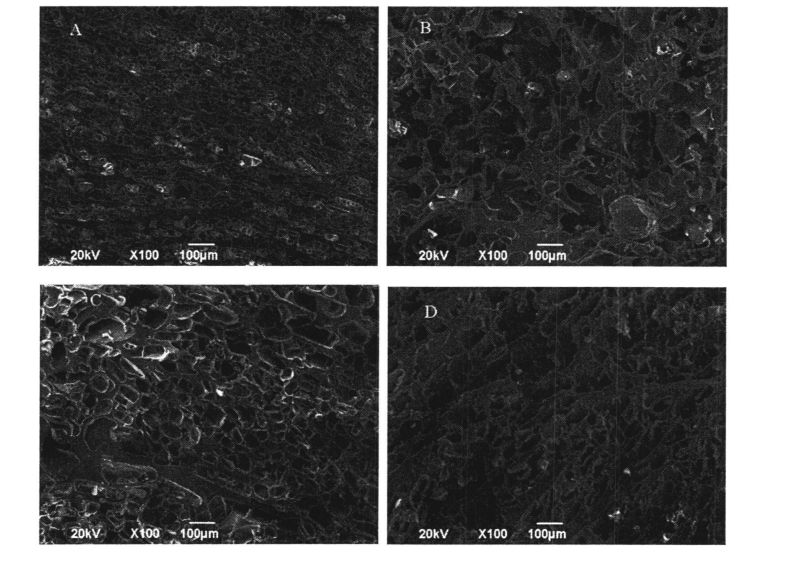
ਇਸ ਪ੍ਰਯੋਗ ਨੇ ਗਿੱਲੀ ਗਲੂਟਨ ਆਟੇ ਅਤੇ ਫਜ਼ਿੰਗ ਸਟੋਰੇਜ (0%, 0.5%, 1%, 1% ਅਤੇ 2%) ਨੂੰ ਫਜ਼ਿੰਗ ਸਟੋਰੇਜ (0, 15, 30 ਅਤੇ 60 ਦਿਨ) ਜੋੜ ਕੇ ਐਚਪੀਐਮਸੀ ਦੀ ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤੀ ਕੀਤੀ. ਵਿਸ਼ੇਸ਼ਤਾਵਾਂ, ਥਰਮੋਡਾਇਨਾਮਿਕ ਵਿਸ਼ੇਸ਼ਤਾਵਾਂ ਅਤੇ ਫਿਜ਼ੀਕੋਕਲਿਕਲ ਗੁਣਾਂ ਦੇ ਪ੍ਰਭਾਵ. The study found that the change and redistribution of water state during the freezing storage process significantly increased the freezable water content in the wet gluten system, which led to the destruction of the gluten structure due to the formation and growth of ice crystals, and ultimately caused the processing properties of the dough to be different. ਉਤਪਾਦ ਦੀ ਗੁਣਵੱਤਾ ਦਾ ਵਿਗਾੜ. The results of frequency scanning showed that the elastic modulus and viscous modulus of the wet gluten mass without adding HPMC decreased significantly during the freezing storage process, and the scanning electron microscope showed that its microstructure was damaged. The content of free sulfhydryl group was significantly increased, and its hydrophobic group was more exposed, which made the thermal denaturation temperature and surface hydrophobicity of gluten protein significantly increased. However, the experimental results show that the addition of I-IPMC can effectively inhibit the changes in the structure and properties of wet gluten mass and gluten protein during freezing storage, and within a certain range, this inhibitory effect is positively correlated with the addition of HPMC. This is because HPMC can reduce the mobility of water and limit the increase of the freezable water content, thereby inhibiting the recrystallization phenomenon and keeping the gluten network structure and the spatial conformation of the protein relatively stable. This shows that the addition of HPMC can effectively maintain the integrity of the frozen dough structure, thereby ensuring product quality.
Starch is a chain polysaccharide with glucose as the monomer. key) two types. From a microscopic point of view, starch is usually granular, and the particle size of wheat starch is mainly distributed in two ranges of 2-10 pro (B starch) and 25-35 pm (A starch). ਕ੍ਰਿਸਟਲ ਬਣਤਰ ਦੇ ਪਰਿਪੇਖ ਤੋਂ, ਕ੍ਰਿਸਟਲਲਾਈਨ ਦੇ ਖੇਤਰ ਅਤੇ ਅਮੋਰਪਸ ਖੇਤਰਾਂ (ਜੇ, ਗੈਰ-ਕ੍ਰਿਸਟਲਲਾਈਨ ਖੇਤਰਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਵੰਡਿਆ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ). Generally, the crystalline region consists of amylopectin and the amorphous region consists mainly of amylose. This is because, in addition to the C chain (main chain), amylopectin also has side chains composed of B (Branch Chain) and C (Carbon Chain) chains, which makes amylopectin appear "tree-like" in raw starch. The shape of the crystallite bundle is arranged in a certain way to form a crystal.
Starch is one of the main components of flour, and its content is as high as about 75% (dry basis). At the same time, as a carbohydrate widely present in grains, starch is also the main energy source material in food. In the dough system, starch is mostly distributed and attached to the network structure of gluten protein. ਪ੍ਰੋਸੈਸਿੰਗ ਅਤੇ ਸਟੋਰੇਜ ਦੇ ਦੌਰਾਨ, ਅਕਸਰ ਜੈਲੇਟਿਨਾਈਜ਼ੇਸ਼ਨ ਅਤੇ ਬੁ aging ਾਪੇ ਦੇ ਪੜਾਅ ਲੰਘਦੇ ਹਨ.
Among them, starch gelatinization refers to the process in which starch granules are gradually disintegrated and hydrated in a system with high water content and under heating conditions. It can be roughly divided into three main processes. 1) Reversible water absorption stage; before reaching the initial temperature of gelatinization, the starch granules in the starch suspension (Slurry) keep their unique structure unchanged, and the external shape and internal structure basically do not change. ਸਿਰਫ ਬਹੁਤ ਘੱਟ ਘੁਲਣਸ਼ੀਲ ਸਟਾਰਚ ਨੂੰ ਪਾਣੀ ਵਿੱਚ ਖਿੰਡਾ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਗਿਆ ਹੈ ਅਤੇ ਇਸ ਨੂੰ ਇਸ ਦੀ ਅਸਲ ਸਥਿਤੀ ਤੇ ਬਹਾਲ ਕੀਤਾ ਜਾ ਸਕਦਾ ਹੈ. 2) The irreversible water absorption stage; as the temperature increases, water enters the gap between the starch crystallite bundles, irreversibly absorbs a large amount of water, causing the starch to swell, the volume expands several times, and the hydrogen bonds between the starch molecules are broken. It becomes stretched and the crystals disappear. At the same time, the birefringence phenomenon of starch, that is, the Maltese Cross observed under a polarizing microscope, begins to disappear, and the temperature at this time is called the initial gelatinization temperature of starch. 3) Starch granule disintegration stage; starch molecules completely enter the solution system to form starch paste (Paste/Starch Gel), at this time the viscosity of the system is the largest, and the birefringence phenomenon completely disappears, and the temperature at this time is called the complete starch gelatinization temperature, the gelatinized starch is also called α-starch [141]. ਜਦੋਂ ਆਟੇ ਪਕਾਏ ਜਾਣ ਤੇ, ਸਟਾਰਚ ਦਾ ਜੈਲੇਟਿਨਾਈਜ਼ੇਸ਼ਨਾਈਜ਼ੇਸ਼ਨਾਈਜ਼ੇਸ਼ਨ ਇਸ ਦੀ ਵਿਲੱਖਣ ਬਣਤਰ, ਸੁਆਦ, ਰੰਗ ਅਤੇ ਪ੍ਰੋਸੈਸਿੰਗ ਵਿਸ਼ੇਸ਼ਤਾਵਾਂ ਨਾਲ ਭੋਜਨ ਨੂੰ ਵਰਤਦਾ ਹੈ.
ਡੀਐਚਜੀ. 9070A Blast Drying Oven
ਨਿਰਮਾਤਾ
Draw 1.5 mL of sample solution and add it to the center of the rheometer sample stage, measure the gelatinization properties of the sample according to the above program parameters, and obtain the time (min) as the abscissa, the viscosity (Pa s) and the temperature (°C) as the starch gelatinization curve of the ordinate. According to GB/T 14490.2008 [158], the corresponding gelatinization characteristic indicators—gelatinization peak viscosity (field), peak temperature (Ang), minimum viscosity (high), final viscosity (ratio) and decay value (Breakdown) are obtained. Value, BV) and regeneration value (Setback Value, SV), wherein, decay value = peak viscosity - minimum viscosity; ਸੈੱਟਬੈਕ ਵੈਲਯੂ = ਅੰਤਮ ਲੇਸ - ਘੱਟੋ ਘੱਟ ਲੇਸ. ਹਰ ਨਮੂਨੇ ਨੂੰ ਤਿੰਨ ਵਾਰ ਦੁਹਰਾਇਆ ਗਿਆ ਸੀ.
(2) ਸਟਾਰਚ ਪੇਸਟ ਦਾ ਸਥਿਰ ਪ੍ਰਵਾਹ ਟੈਸਟ
Take 1.5 mL of sample solution and place it on the sample stage of the rheometer (Discovery.R3), press down the 40 m/n plate with a diameter of 1500 mm, and remove the excess sample solution, and continue to lower the plate to 1000 mm, on motor, the speed was set to 5 rad/s and rotated for 1 min to fully homogenize the sample solution and avoid the sedimentation of starch granules. ਤਾਪਮਾਨ ਸਕੈਨ 25 ਡਿਗਰੀ ਸੈਲਸੀਅਸ ਤੋਂ ਸ਼ੁਰੂ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ਅਤੇ 5 ਤੇ ਖਤਮ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ. ਸੀ / ਮਿੰਟ ਨੂੰ 95 ਡਿਗਰੀ ਸੈਲਸੀਅਸ ਤੇ ਕੀਤਾ ਗਿਆ, ਅਤੇ ਫਿਰ 5 ਡਿਗਰੀ ਸੈਲਸੀਅਸ ਵਿੱਚ 5 "ਸੀ / ਮਿੰਟ ਤੇ ਘੱਟ ਕੀਤਾ ਗਿਆ.
A layer of petrolatum was lightly applied to the edge of the starch gel obtained above to avoid water loss during subsequent experiments. ਅਬੇਬੇ & ਰੋਂਡਾ method ੰਗ [1601] ਦਾ ਜ਼ਿਕਰ ਕਰਨਾ ਪਹਿਲਾਂ ਹੀ ਲਕੀਰ ਵਿਸਕੋਲੇਟਿਟੀ ਖੇਤਰ (ਐਲਵੀਪੀ) ਦਾ ਪਤਾ ਲਗਾਉਣ ਲਈ ਕੀਤਾ ਗਿਆ ਸੀ, ਦੀ ਬਾਰੰਬਾਰ (10 ਮਿੰਟ ਲਈ 25 ° ਸੈਂ.
After the corresponding freezing treatment time, the samples were taken out, thawed completely, and dried in an oven at 40 °C for 48 h. Finally, it was ground through a 100-mesh sieve to obtain a solid powder sample for use (suitable for XRD testing). Xie ਵੇਖੋ, ਅਤੇ A1. (2014) method for sample preparation and determination of thermodynamic properties '1611, weigh 10 mg of starch sample into a liquid aluminum crucible with an ultra-micro analytical balance, add 20 mg of distilled water in a ratio of 1:2, press and seal it and place it at 4 °C In the refrigerator, equilibrated for 24 h. Freeze at 18°C (0, 15, 30 and 60 days). Add 0.5%, 1%, 2% (w/w) HPMC to replace the corresponding quality of starch, and other preparation methods remain unchanged. After the freezing storage time is over, take out the crucible and equilibrate at 4 °C for 4 h.
(3) ਜੈਲੇਟਿਨਾਈਜ਼ੇਸ਼ਨ ਤਾਪਮਾਨ ਅਤੇ ਐਜਲਪੀ ਤਬਦੀਲੀ ਦਾ ਨਿਰਣਾਇਕ
Take 0.1 g of the dried, ground and sieved amyloid into a 50 mL centrifuge tube, add 10 mL of distilled water to it, shake it well, let it stand for 0.5 h, and then place it in a 95°C water bath at a constant temperature. After 30 min, after gelatinization is complete, take out the centrifuge tube and place it in an ice bath for 10 min for rapid cooling. ਅੰਤ ਵਿੱਚ, 20 ਮਿੰਟ ਲਈ 5000 RPM ਤੇ ਸੈਂਟੀਫਿਫਿ ume ਗ ਜੇਲਟ, ਅਤੇ ਇੱਕ ਅਸ਼ੁੱਧਤਾ ਨੂੰ ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤ ਕਰਨ ਲਈ ਅਲੌਕਿਕ ਡੋਲ੍ਹ ਦਿਓ. Swelling Power=precipitation mass/sample mass [163].
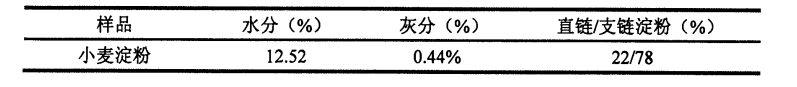
4.3.2 ਐਚਪੀਐਮਸੀ ਜੋੜਨ ਦੇ ਪ੍ਰਭਾਵਾਂ ਦੇ ਜੈਲੇਟਿਨਾਈਜ਼ੇਸ਼ਨ ਵਿਸ਼ੇਸ਼ਤਾਵਾਂ ਦੇ ਜੈਲੇਟਿਨਾਈਜ਼ੇਸ਼ਨ ਵਿਸ਼ੇਸ਼ਤਾਵਾਂ ਦੇ ਜੈਲੇਟਿਨੀਕਰਣ ਵਿਸ਼ੇਸ਼ਤਾਵਾਂ ਦੇ ਸਮੇਂ ਦੇ ਅੰਤ ਵਿੱਚ
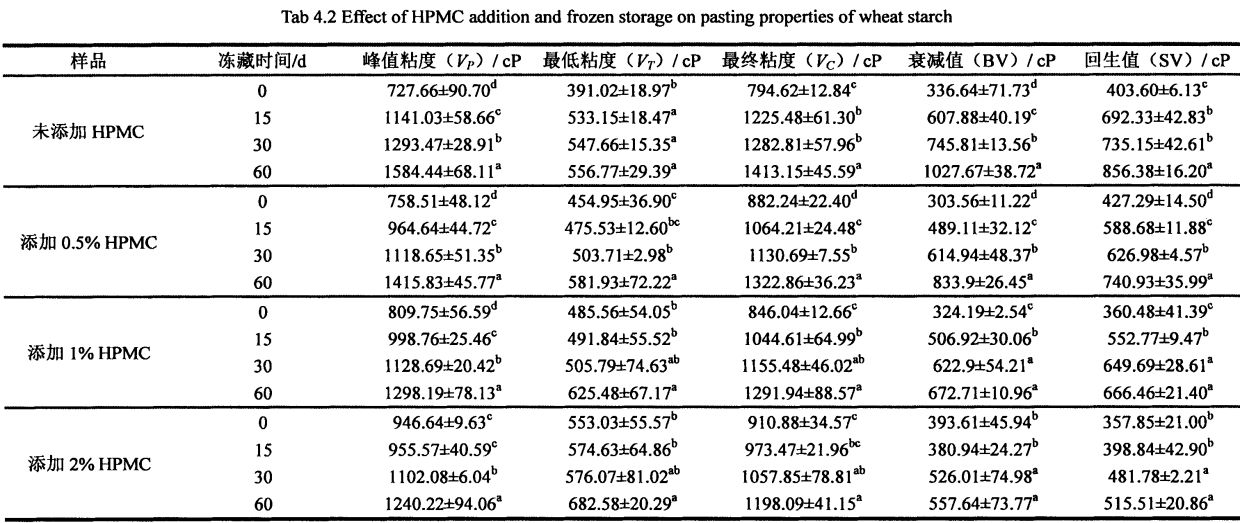
(Frozen storage for 0 days) increased to 1198.09 ± 41.15 CP (frozen storage for 60 days). Correspondingly, the attenuation value of starch suspension without adding HPMC increased from 336.64 ± 71.73 CP (frozen storage for 0 days) to 1027.67 ± 38.72 CP (frozen storage for 60 days); 0.5% hphar ਸਸਪੈਂਸ਼ਨ ਦੇ ਅਟੂਨਤਾ ਮੁੱਲ ਨੂੰ% hpmc ਨਾਲ ਵਧਾ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਗਿਆ 303.56 ± 11.22 ਸੀਪੀ (0 ਦਿਨਾਂ ਲਈ ਜੰਮਿਆ ਸਟੋਰੇਜ) ਤੋਂ ਵਧਾ ਕੇ 833.915 ਸੀਪੀ (60 ਦਿਨਾਂ ਲਈ ਜੰਮੀ ਸਟੋਰੇਜ) ਵਿੱਚ ਵਾਧਾ ਹੋਇਆ; 1% ਐਚਪੀਪੀਸੀ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ ਸਟਾਰਚ ਮੁਅੱਤਲ ਸ਼ਾਮਲ ਕੀਤੇ ਗਏ ਵੈਲਯੂ ਦੇ ਵੈਲਯੂ ਦਾ ਮੁੱਲ 324.19 ± 2.54 ਸੀਪੀ (0 ਦਿਨਾਂ ਲਈ ਠੰਡ) ਤੋਂ ਵਧਾ ਕੇ 10.96 ਸੀਪੀ (60 ਦਿਨਾਂ ਲਈ ਠੰ.) ਵਿੱਚ ਵਾਧਾ ਕੀਤਾ ਗਿਆ ਸੀ; 2% hpיc ਜੋੜਦੇ ਸਮੇਂ, ਸਟਾਰਚ ਮੁਅੱਤਲ ਦਾ ਅਟੁੱਟ ਮੁੱਲ 393.61 ± 45.94 ਸੀਪੀ (60 ਦਿਨਾਂ ਲਈ ਠੰਡ) ਤੋਂ ਵਧਾ ਕੇ 557.64 ± 73.77 ਸੀਪੀ (ਠੰਡੇ) ਕਰ ਕੇ. while the starch suspension without HPMC added The retrogradation value increased from 403.60 ± 6.13 C
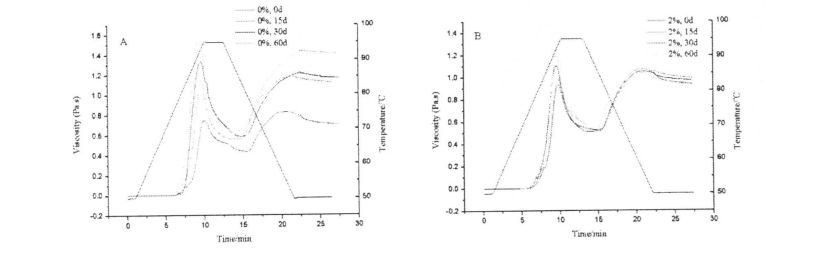
ਤਰਲ ਪਦਾਰਥਾਂ ਦੇ ਸਪੱਸ਼ਟ ਲੇਸ (ਸ਼ੀਅਰ ਲੇਸ) ਦੇ ਪ੍ਰਭਾਵ ਨੂੰ ਸਥਿਰ ਪ੍ਰਵਾਹ ਟੈਸਟ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਜਾਂਚ ਕੀਤੀ ਗਈ ਸੀ, ਅਤੇ ਤਰਲ ਪਦਾਰਥਾਂ ਦੀ ਸਮੱਗਰੀ structure ਾਂਚਾ ਅਤੇ ਗੁਣਾਂ ਪ੍ਰਤੀਬਿੰਬਿਤ ਕੀਤੀ ਗਈ ਸੀ. Table 4.3 lists the equation parameters obtained by nonlinear fitting, that is, the consistency coefficient K and the flow characteristic index D, as well as the influence of the addition amount of HPMC and the freezing storage time on the above parameters K gate.
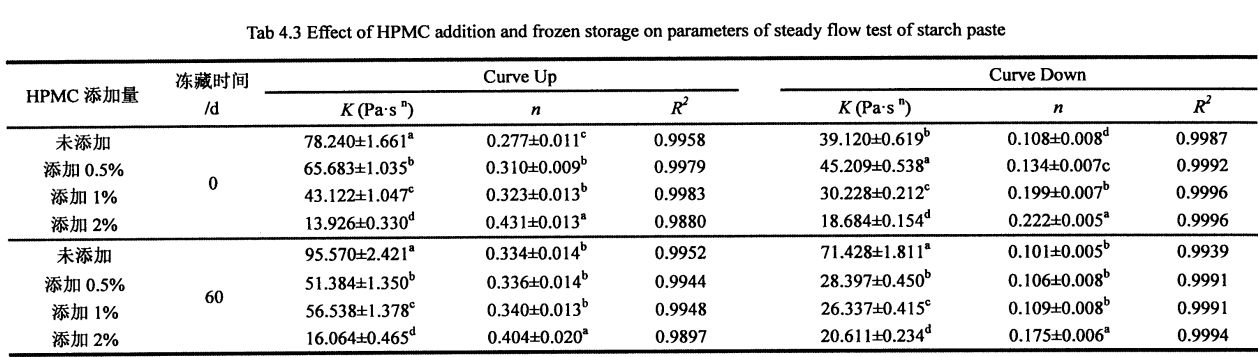
On the other hand, for the starch without frozen storage, its K value decreased significantly with the addition of HPMC, from 78.240±1.661 Pa ·sn (without adding HPMC) to 65.240±1.661 Pa ·sn (without adding HPMC), respectively. 683±1.035 Pa ·sn (add 0.5% Hand MC), 43.122±1.047 Pa ·sn (add 1% HPMC), and 13.926±0.330Pa·Sn (add 2% HPMC), while the n value increased significantly, from 0.277 ± 0.011 (without adding HPMC) to 0.277 ± 0.011 in turn. 310 ± 0.009 (0.5% ਐਚਪੀਪੀਸੀ ਸ਼ਾਮਲ ਕਰੋ), ਓ. 0.513 (2% ਐਚਪੀਪੀਐਸ ਸ਼ਾਮਲ ਕਰੋ) ਅਤੇ ਐਨ ਵੈਲਿਨ (2008) ਦੇ ਵਾਧੇ ਦੇ ਸਮਾਨ ਹਨ HPMC makes the fluid has a tendency to change from pseudoplastic to Newtonian [168'1691]. at the same time, For the starch stored frozen for 60 days, the K, n values showed the same change rule with the increase of HPMC addition.
However, with the prolongation of freezing storage time, the values of K and n increased to different degrees, among which the value of K increased from 78.240 ± 1.661 Pa·sn (unadded, 0 days) to 95.570 ± 1, respectively. 2.421 Pa·sn (no addition, 60 days), increased from 65.683±1.035 Pa ·S n (addition of O. 5% HPMC, 0 days) to 51.384±1.350 Pa ·S n (Add to 0.5% HPMC, 60 days), increased from 43.122±1.047 Pa ·sn (adding 1% HPMC, 0 days) to 56.538±1.378 Pa ·sn (adding 1% HPMC, 60 days) ), and increased from 13.926 ± 0.330 Pa ·sn (adding 2% HPMC, 0 days) to 16.064 ± 0.465 Pa ·sn (adding 2% HPMC, 60 days); 0.277 ± 0.011 (without adding HPMC, 0 days) rose to O. 334±0.014 (no addition, 60 days), increased from 0.310±0.009 (0.5% HPMC added, 0 day) to 0.336±0.014 (0.5% HPMC added, 60 days), from 0.323 ± 0.013 (add 1% HPMC, 0 days) to 0.340 ± 0.013 (add 1% HPMC, 60 days), and from 0.431 ± 0.013 (add 1% HPMC, 60 days) 2% HPMC, 0 days) to 0.404+0.020 (add 2% HPMC, 60 days). By comparison, it can be found that with the increase of the addition amount of HPMC, the change rate of K and Knife value decreases successively, which shows that the addition of HPMC can make the starch paste stable under the action of shearing force, which is consistent with the measurement results of starch gelatinization characteristics. ਇਕਸਾਰ.
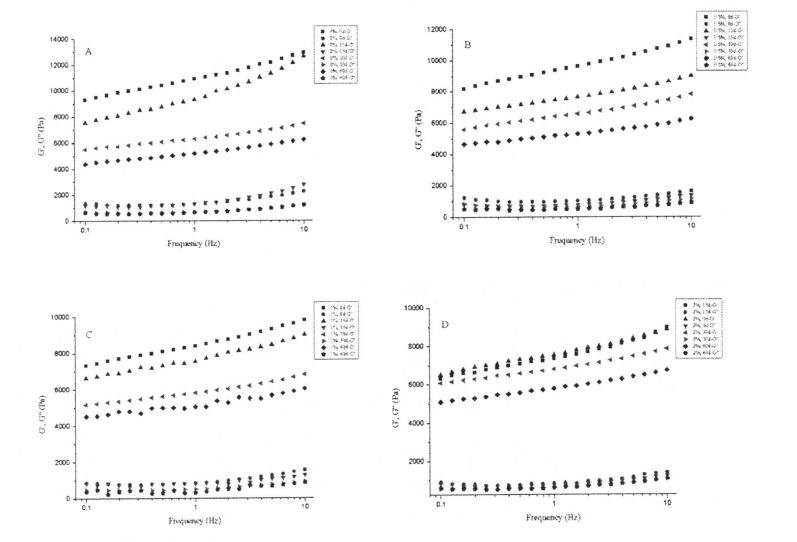
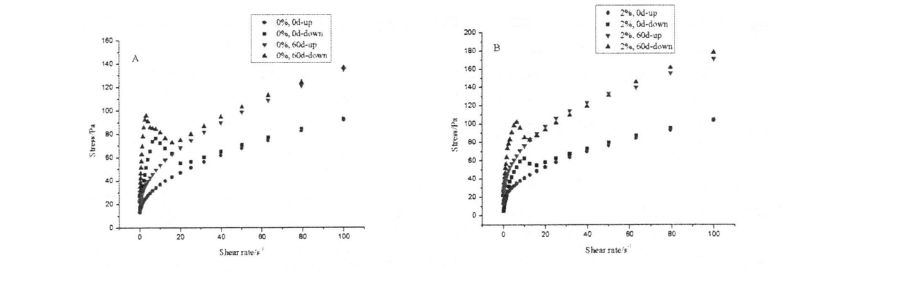
ਸ੍ਟ੍ਰੀਟਸਟੇਟ ਪੇਸਟ ਦੇ ਲਚਕੀਲੇ ਅਤੇ ਲੇਸਦਾਰ ਮਾਡਲਾਂ 'ਤੇ ਐਚਪੀਐਮ ਦੇ 4.3 ਪ੍ਰਭਾਵ ਅਤੇ ਫ੍ਰੋਜ਼ਨ ਸਟੋਰੇਜ' ਤੇ ਜੰਮਿਆ ਹੋਇਆ ਹੈ
Note: A is the change of viscoelasticity of unadded HPMC starch with the extension of freezing storage time; ਬੀ ਓ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ ਰੁਕਣ ਵਾਲੇ ਸਟੋਰੇਜ ਸਟਾਰਚ ਦੇ ਵਿਸਥਾਰ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ 5% ਐਚਪੀਐਮਸੀ ਸਟਾਰਚ ਦੀ ਵਿਜ਼ਕੋਲੇਟਿਟੀ ਦੀ ਤਬਦੀਲੀ ਦੀ ਤਬਦੀਲੀ; C is the change of the viscoelasticity of 1% HPMC starch with the extension of freezing storage time; D is the change of the viscoelasticity of 2% HPMC starch with the extension of freezing storage time
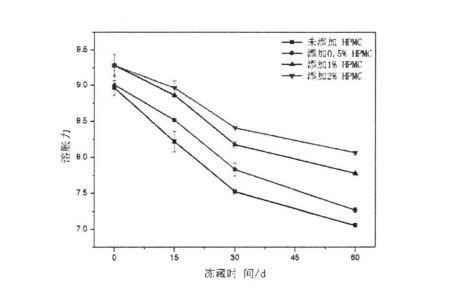
The swelling ratio of starch can reflect the size of starch gelatinization and water swelling, and the stability of starch paste under centrifugal conditions. As shown in Figure 4.4, for starch without frozen storage, with the increase of HPMC addition, the swelling force of starch increased from 8.969+0.099 (without adding HPMC) to 9.282- -L0.069 (adding 2% HPMC), which shows that the addition of HPMC increases the swelling water absorption and makes starch more stable after gelatinization, which is consistent with the conclusion of starch gelatinization characteristics. However, with the extension of frozen storage time, the swelling power of starch decreased. . .007 (ਕੋਈ ਐਚਪੀਐਮਸੀ ਸ਼ਾਮਲ ਨਹੀਂ ਹੋਇਆ), 9.007 + 0.147 ਤੋਂ 7.284-4-4-0.08 ਤੋਂ ਘਟਾ ਕੇ 7.0.59 ਤੋਂ 8.064 + 0.069 ਤੱਕ ਘਟਾ ਦਿੱਤਾ ਗਿਆ. The results showed that the starch granules were damaged after freezing storage, resulting in the precipitation of part of the soluble starch and centrifugation. Therefore, the solubility of starch increased and the swelling power decreased. In addition, after freezing storage, starch gelatinized starch paste, its stability and water holding capacity decreased, and the combined action of the two reduced the swelling power of starch [1711]. On the other hand, with the increase of HPMC addition, the decline of starch swelling power gradually decreased, indicating that HPMC can reduce the amount of damaged starch formed during freezing storage and inhibit the degree of starch granule damage.
The gelatinization of starch is an endothermic chemical thermodynamic process. Therefore, DSC is often used to determine the onset temperature (Dead), peak temperature (To), end temperature (T p), and gelatinization enthalpy of starch gelatinization. (ਟੀਸੀ). Table 4.4 shows the DSC curves of starch gelatinization with 2% and without HPMC added for different freezing storage times.
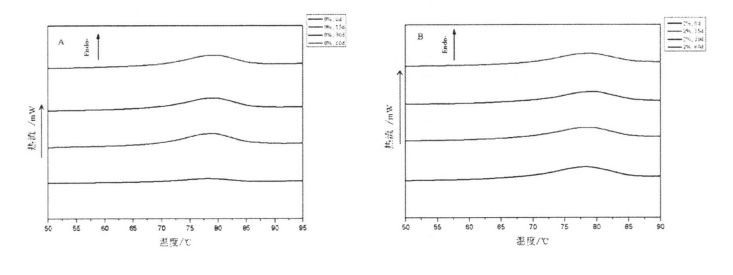
ਜਿਵੇਂ ਕਿ ਐਚਪੀਐਮਸੀ ਜੋੜ ਦੇ ਵਾਧੇ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ, ਤਾਜ਼ੇ ਐਮੀਲਾਈਡ ਲਈ ਦਰਸਾਇਆ ਗਿਆ ਹੈ, 77.528 ± 0.051 (0.042), ਅਤੇ 78.606 ± 0.051 (2% ਸ਼ਾਮਲ ਕਰੋ (2% ਸ਼ਾਮਲ ਕਰੋ) HPMC), but 4H is significant Decrease, from 9.450 ± 0.095 (without adding HPMC) to 8.53 ± 0.030 (adding 0.5% HPMC), 8.242A: 0.080 (adding 1% HPMC) and 7 .736 ± 0.066 (add 2% HPMC). This is similar to Zhou, et a1. (2008) found that adding a hydrophilic colloid decreased the starch gelatinization enthalpy and increased the starch gelatinization peak temperature [172]. This is mainly because HPMC has better hydrophilicity and is easier to combine with water than starch. At the same time, due to the large temperature range of the thermally accelerated gelation process of HPMC, the addition of HPMC increases the peak gelatinization temperature of starch, while the gelatinization Enthalpy decreases.
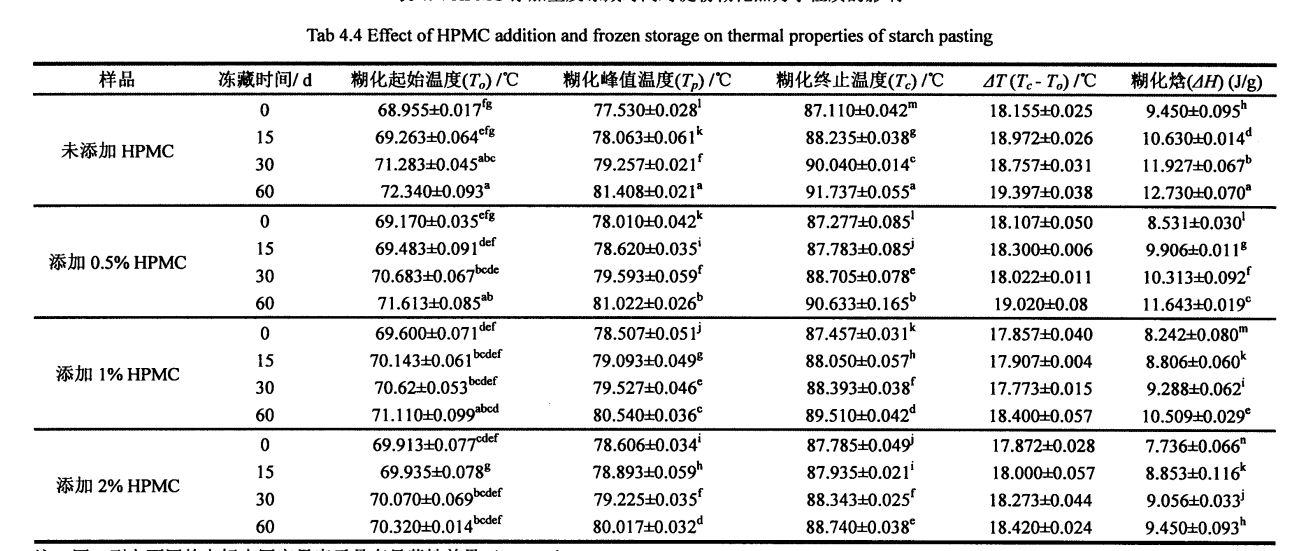
X. ਐਕਸ-ਰੇ ਡਿਵੈਸ਼ਨ (ਐਕਸਆਰਡੀ) ਦੁਆਰਾ ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤ ਕੀਤਾ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ਇੱਕ ਖੋਜ ਵਿਧੀ ਹੈ ਜੋ ਜਾਣਕਾਰੀ ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤ ਕਰਨ ਲਈ ਸਮੱਗਰੀ, ਬਣਤਰ ਜਾਂ ਮੌਰਫੋਲੋਜੀ ਜਾਂ ਸਮੱਗਰੀ ਦੇ ਅਣੂ ਜਾਂ ਅਣੂਆਂ ਦੇ ਰੂਪ ਵਿਗਿਆਨ ਜਾਂ ਅਣਉਲੋਲੋਜੀ ਦੀ ਰਚਨਾ ਨੂੰ ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤ ਕਰਨ ਲਈ ਵਿਗਾੜ ਸਪੈਕਟ੍ਰਮ ਦਾ ਵਿਸ਼ਲੇਸ਼ਣ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ. Because starch granules have a typical crystalline structure, XRD is often used to analyze and determine the crystallographic form and relative crystallinity of starch crystals.
However, with the prolongation of freezing storage time, the relative crystallinity of starch increased from 20.40 + 0.14 (without HPMC, 0 days) to 36.50 ± 0.42 (without HPMC, frozen storage, respectively). 60 days), and increased from 25.75 + 0.21 (2% HPMC added, 0 days) to 32.70 ± 0.14 (2% HPMC added, 60 days) (Figure 4.6.B), this and Tao, et a1. (2016), ਮਾਪ ਦੇ ਨਤੀਜਿਆਂ ਦੇ ਪਰਿਵਰਤਨ ਨਿਯਮ ਇਕਸਾਰ ਹਨ [173-174]. The increase in relative crystallinity is mainly caused by the destruction of the amorphous region and the increase in the crystallinity of the crystalline region. In addition, consistent with the conclusion of the changes in the thermodynamic properties of starch gelatinization, the addition of HPMC reduced the degree of relative crystallinity increase, which indicated that during the freezing process, HPMC could effectively inhibit the structural damage of starch by ice crystals and maintain the Its structure and properties are relatively stable.
ਖਮੀਰ ਇਕ ਯੂਨੀਸੁਕਲਿਕੂਲੋਟਿਕ ਸੂਖਮ ਜੀਵ-ਵਿਗਿਆਨਕ ਹੈ, ਇਸ ਦੇ ਸੈੱਲ ਦੇ structure ਾਂਚੇ ਵਿਚ ਸੈੱਲ ਦੀ ਕੰਧ, ਅਤੇ ਮਾਈਟੋਚੌਂਦਰੀਆ, ਆਦਿ ਸ਼ਾਮਲ ਹਨ. Under anaerobic conditions, it produces alcohol and energy, while under aerobic conditions it metabolizes to produce carbon dioxide, water and energy.
ਸਮੱਗਰੀ ਅਤੇ ਯੰਤਰ
ਨਿਰਮਾਤਾ
ਜਿਆਨਸੂ ਟਾਂਗਜਿੰਗ ਸ਼ੁਟੀਕਰਨ ਉਪਕਰਣ ਸਹਿ, ਲਿਮਟਿਡ
Weigh 3 g of active dry yeast, add it to a sterilized 50 mL centrifuge tube under aseptic conditions, and then add 27 mL of 9% (w/V) sterile saline to it, shake it up, and prepare 10% (w/w) yeast broth. Then, quickly move to. Store in a refrigerator at 18°C. 15 ਡੀ, 30 ਡੀ, ਅਤੇ ਜੁਰਮਾਨਾ ਭੰਡਾਰਨ ਤੋਂ ਬਾਅਦ, ਨਮੂਨਿਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਟੈਸਟ ਕਰਨ ਲਈ ਬਾਹਰ ਕੱ .ਿਆ ਗਿਆ. Add 0.5%, 1%, 2% HPMC (w/w) to replace the corresponding percentage of active dry yeast mass. In particular, after the HPMC is weighed, it must be irradiated under an ultraviolet lamp for 30 minutes for sterilization and disinfection.
Weigh 1 g of dough, add it to a test tube with 9 mL of sterile normal saline according to the requirements of the aseptic operation, shake it fully, record the concentration gradient as 101, and then dilute it into a series of concentration gradients until 10'1. ਉਪਰੋਕਤ ਟੱਬਾਂ ਵਿੱਚੋਂ 1 ਮਿ.ਲੀ. ਘੱਟ ਜਾਣ ਦਾ 1 ਮਿ.ਲੀ.ਲੀਬਿਨ ਬਣਾਓ, ਇਸਨੂੰ 3 ਐਮ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਨਿਰਧਾਰਤ ਓਪਰੇਟਿੰਗ ਜ਼ਰੂਰਤਾਂ ਅਤੇ ਸਭਿਆਚਾਰਕ ਾਂਚਿਆਂ ਦੇ ਅਨੁਸਾਰ 25 ਡਿਗਰੀ ਸੈਲਸੀਅਸ ਇਨਯੂਟੇਟਰ ਵਿੱਚ ਰੱਖੋ. 5 d, take out after the end of the culture, first observe the colony morphology to determine whether it conforms to the colony characteristics of yeast, and then count and microscopically examine [179]. Each sample was repeated three times.
The proofing height of dough is often affected by the combined effect of yeast fermentation gas production activity and dough network structure strength. Among them, yeast fermentation activity will directly affect its ability to ferment and produce gas, and the amount of yeast gas production determines the quality of fermented flour products, including specific volume and texture. ਖਮੀਰ ਦੀ ਫਰਮੈਂਟੇਸ਼ਨ ਗਤੀਵਿਧੀ ਮੁੱਖ ਤੌਰ 'ਤੇ ਬਾਹਰੀ ਕਾਰਕਾਂ ਦੁਆਰਾ ਪ੍ਰਭਾਵਤ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ (ਜਿਵੇਂ ਕਿ ਪੋਬੋਨ ਅਤੇ ਨਾਈਟ੍ਰੋਜਨ ਸਰੋਤ, ਤਾਪਮਾਨ, ਪੀਐਚਏਈਟੀਈਏਟੀਏਈਐਸ, ਆਦਿ ਦੇ ਚੱਕਰ, ਗਤੀਵਿਧੀ).

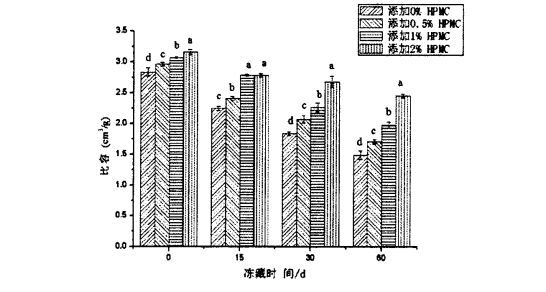
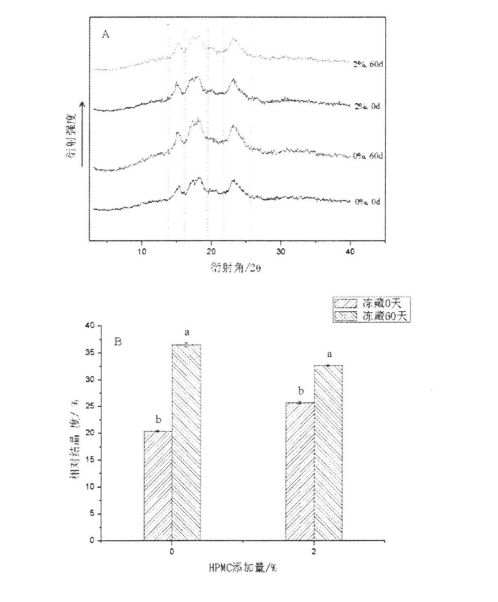
As shown in Figure 5.1, when frozen for 0 days, with the increase in the amount of HPMC added, the proofing height of the dough increased from 4.234-0.11 cm to 4.274 cm without adding HPMC. -0.12 cm (0.5% HPMC added), 4.314-0.19 cm (1% HPMC added), and 4.594-0.17 cm (2% HPMC added) This may be mainly due to HPMC Addition changes the properties of the dough network structure (see Chapter 2). ਹਾਲਾਂਕਿ, 60 ਦਿਨਾਂ ਲਈ ਜੰਮਣ ਤੋਂ ਬਾਅਦ, ਆਟੇ ਦੀ ਪਰਮਾਣਕਿ ਉਚਾਈ ਡਿਗਰੀਆਂ ਵੱਖ ਵੱਖ ਕਰਨ ਲਈ ਘਟੀ. Specifically, the proofing height of the dough without HPMC was reduced from 4.234-0.11 cm (freezing for 0 days) to 3 .18+0.15 cm (frozen storage for 60 days); the dough added with 0.5% HPMC was reduced from 4.27+0.12 cm (frozen storage for 0 days) to 3.424-0.22 cm (frozen storage for 0 days). 60 days); the dough added with 1% HPMC decreased from 4.314-0.19 cm (frozen storage for 0 days) to 3.774-0.12 cm (frozen storage for 60 days); while the dough added with 2% HPMC woke up. The hair height was reduced from 4.594-0.17 cm (frozen storage for 0 days) to 4.09-±0.16 cm (frozen storage for 60 days). It can be seen that with the increase of the addition amount of HPMC, the degree of decrease in the proofing height of the dough gradually decreases. This shows that under the condition of frozen storage, HPMC can not only maintain the relative stability of the dough network structure, but also better protect the survival rate of yeast and its fermentation gas production activity, thereby reducing the quality deterioration of fermented noodles.
In the case of frozen storage, since the frozen water in the dough system is converted into ice crystals, the osmotic pressure outside the yeast cells is increased, so that the protoplasts and cell structures of the yeast are under a certain degree of stress. ਜਦੋਂ ਤਾਪਮਾਨ ਘੱਟ ਜਾਂ ਘੱਟ ਤਾਪਮਾਨ ਤੇ ਘੱਟ ਤਾਪਮਾਨ ਤੇ ਰੱਖਿਆ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ, ਤਾਂ ਖਮੀਰ ਦੇ ਸੈੱਲ ਤਰਲ, ਸੈੱਲ ਦੇ ਤਰਲ ਪਦਾਰਥਾਂ ਦੀ ਅਤਿਕਾਰੇ ਦੇ ਵਿਛੜਣ ਵਾਲੇ, ਜਿਵੇਂ ਕਿ ਗਲੂਥੋਥੋਨੀਓਨ, ਜਾਂ ਪੂਰੀ ਮੌਤ ਦੇ ਰਿਲੀਜ਼ਗੀ ਦੇ ਵਿਨਾਸ਼ ਵੱਲ ਅਗਵਾਈ ਕਰਨਗੇ; ਉਸੇ ਸਮੇਂ, ਖਮੀਰ ਵਾਤਾਵਰਣ ਦੇ ਤਣਾਅ ਦੇ ਅਧੀਨ, ਆਪਣੀ ਪਾਚਕ ਕਿਰਿਆ ਨੂੰ ਘਟਾਇਆ ਜਾਵੇਗਾ, ਅਤੇ ਕੁਝ ਸਪੋਰਸ ਤਿਆਰ ਕੀਤੇ ਜਾਣਗੇ, ਜੋ ਖਮੀਰ ਦੇ ਫਰਮੈਂਟੇਸ਼ਨ ਨੂੰ ਗੈਸ ਉਤਪਾਦਨ ਦੀਆਂ ਗਤੀਵਿਧੀਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਘਟਾ ਦੇਵੇਗਾ.
ਪੋਸਟ ਦਾ ਸਮਾਂ: ਅਕਤੂਬਰ- 08-2022